Let’s be real for a second—medical billing can feel like you’re trying to crack a secret code sometimes. And when you throw in specific place of service codes like POS 49? Well, that’s when even experienced billers start scratching their heads.
I get it. You’re already dealing with insurance companies that love to deny claims for the smallest reasons. The last thing you need is another headache about whether you picked the right code. But here’s some good news: POS 49 isn’t nearly as complicated as it might seem once someone breaks it down for you in plain English.
So whether you’re new to medical billing or you’ve been doing this for years and just want a refresher, let’s talk about POS 49 like real people—no corporate jargon, no confusing technical talk. Just straight answers that’ll help you get claims paid faster.
Understanding POS 49: What Does It Really Mean?
Alright, let’s cut through the confusion. Place of service 49 is simply a billing code that tells insurance companies one thing: this service happened at an independent clinic.
Now, what’s an independent clinic? Picture this—it’s not someone’s private doctor’s office, and it’s not part of a big hospital either. It’s somewhere in between. Could be an urgent care center, a community health clinic, or a specialty treatment facility that operates on its own.
Here’s the easiest way to think about it: if the clinic functions independently—meaning it’s not attached to a hospital system and isn’t Dr. Jones’ private practice—then you’re probably looking at a POS 49 situation. That’s really all there is to it at the basic level.
Why Place of Service Codes Matter in Healthcare Billing
You might be sitting there thinking, “Okay, but why do I need to stress about where something happened? Can’t I just bill for the actual service?”
Trust me, I wish it worked that way too. But insurance companies? They want to know everything. And the “where” matters just as much as the “what” when it comes to getting paid.
Here’s why location codes like POS 49 are such a big deal:
Money talks: Insurance companies pay different amounts based on where you provided the service. A procedure at an independent clinic might get reimbursed differently than the same thing at a hospital or doctor’s office.
Speed matters: Use the right code, and your claim sails through. Use the wrong one? Welcome to denial city, population: your claim.
Coverage isn’t universal: Just because a service is covered doesn’t mean it’s covered everywhere. Some insurance plans have specific rules about independent clinics.
Nobody wants an audit: Using incorrect codes is like waving a red flag. Stay accurate, stay compliant, stay out of trouble.
Bottom line? When you slap that POS 49 on a claim, you’re giving the insurance company critical information that affects whether you get paid, how much, and how fast.
POS 49 vs POS 11 Billing: Knowing the Difference
This is where things get messy for a lot of people. Even billers who’ve been doing this for years sometimes pause and think, “Wait, which code do I use here?”
Let me make it crystal clear:
POS 11 = Doctor’s office. That’s it. When someone goes to their family physician’s practice for a checkup or to get that weird rash looked at, that’s POS 11.
POS 49 = Independent clinic. Think bigger than a doctor’s office but not hospital-sized. These places operate on their own terms.
Here’s my foolproof way to remember: Does it feel like you’re going to see “your doctor” at their personal practice? POS 11. Does it feel more like you’re going to a facility that has multiple providers and operates independently? POS 49.
Still confused? You’re not alone. Let me give you some real examples that’ll make it click.
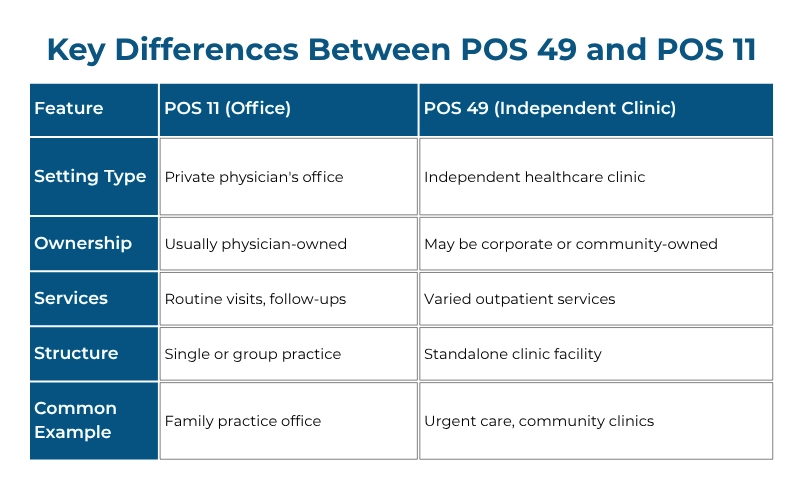
Understanding this distinction is crucial because using the wrong code can lead to claim denials, payment delays, and compliance headaches.
When Should You Use POS 49 for Insurance Claims?
Here’s where things get practical. You should reach for POS 49 when billing for services provided at:
- Urgent care centers operating as independent entities
- Community health clinics not affiliated with hospitals
- Standalone specialty clinics (pain management, physical therapy, etc.)
- Walk-in clinics that function independently
- Retail health clinics in pharmacies or stores (though POS 17 may also apply)
The key question to ask yourself: “Is this facility operating independently from a hospital or physician’s private practice?” If yes, POS 49 is likely your answer.
Real-World Examples of POS 49 Usage
Let’s look at some actual scenarios because that’s how this stuff really makes sense:
Scenario 1: Sarah twists her ankle playing weekend soccer. She doesn’t want to wait days for her regular doctor, so she goes to an urgent care center that’s not connected to any hospital. The staff wraps her ankle and sends her home with crutches. That’s POS 49.
Scenario 2: A community health clinic downtown provides prenatal care for expecting moms who can’t afford private practice fees. The clinic operates independently with its own staff and resources. POS 49 all day.
Scenario 3: Mike needs physical therapy after shoulder surgery. He goes to a standalone rehab clinic that specializes in sports injuries. It’s not part of the hospital where he had surgery, and it’s not his surgeon’s office either. You guessed it—POS 49.
See the pattern? These are all independent facilities doing their own thing, separate from hospitals and private practices.
Common POS 49 Mistakes That’ll Cost You Money
Let’s talk about the mistakes that keep me up at night—or more accurately, the ones that probably keep your revenue cycle manager up at night. These errors are super common, and they cost practices thousands in denied claims every year.
Mistake #1: Mixing Up Hospital Outpatient Departments with Independent Clinics
This one’s tricky. Just because a clinic is in a different building from the hospital doesn’t automatically make it independent. If it’s owned and operated by the hospital system, you’re looking at POS 22, not POS 49.
I’ve seen billers assume that physical distance equals independence. Nope. It’s about ownership and operation. That rehab center might be five miles from the main hospital, but if Hospital XYZ runs it, it’s not getting POS 49.
How to avoid it: Before coding anything, verify the facility’s actual relationship with nearby hospitals. Don’t go by location—go by ownership.
Mistake #2: Getting Fooled by Names
Here’s something that trips people up all the time: a place calls itself “XYZ Clinic,” so everyone assumes it must be POS 49, right? Wrong.
Plenty of physician practices slap the word “clinic” on their sign because it sounds more professional or accessible. But if Dr. Anderson runs it as their private practice, it’s still POS 11—no matter what the sign says.
Don’t let marketing names fool you. Look at the actual structure of the business.
How to avoid it: Ignore what’s on the sign. Check how the facility is registered and operates. Is it a physician’s private practice or an independent facility? That’s your answer.
Mistake #3: Telehealth Confusion
Okay, telehealth threw everyone for a loop when it exploded during the pandemic. Now people are wondering: “If an independent clinic provides telehealth, is that still POS 49?”
Telehealth gets its own set of POS codes. Usually it’s POS 02 if the patient is at home, or POS 10 if they’re using telehealth from their house. The fact that the provider is sitting in an independent clinic doesn’t matter—what matters is where the patient is receiving the service.
How to avoid it: When it’s telehealth, forget about where the provider is located. Code based on where the patient is.
Mistake #4: Sloppy Documentation
You know what kills claims faster than anything? Documentation that doesn’t back up what you’re billing.
Maybe the service really did happen at an independent clinic, but your paperwork just says “clinic visit” with no other details. Insurance companies see that and immediately get suspicious. They want proof that this was actually POS 49 and not something else.
I can’t stress this enough: your documentation needs to clearly show the facility name, address, and its independent status. Otherwise, you’re just asking for denials.
How to avoid it: Make sure every claim has rock-solid documentation. Include specific facility details that prove it qualifies as an independent clinic.
Mistake #5: Ignoring What Your Payer Actually Wants
Here’s something that catches people off guard: not all insurance companies interpret POS 49 exactly the same way. I know, I know—shouldn’t there be one standard definition? You’d think so, but welcome to healthcare billing.
Medicare might be cool with your POS 49 usage, but Blue Cross might have slightly different requirements. And don’t even get me started on how Medicaid rules change from state to state.
How to avoid it: Keep a cheat sheet for each major payer you deal with. Note their specific quirks about POS 49. Yeah, it’s extra work upfront, but it saves you from headaches later.
POS 49 for Insurance Claims: What You Need to Know
When you submit claims with place of service 49, insurance companies process them with certain expectations. Understanding these can help you avoid denials and speed up reimbursement.
How Insurance Companies View POS 49
Insurance carriers use POS codes to:
- Determine appropriate fee schedules: Independent clinics may have different reimbursement rates than physician offices
- Verify network status: They check if the clinic is in-network for the patient’s plan
- Apply correct benefit levels: Patient cost-sharing may differ based on place of service
- Identify potential fraud: Unusual patterns of POS 49 usage may trigger audits
Medicare and POS 49
Medicare recognizes POS 49 for independent clinics, though there are some nuances. Facility services are typically reimbursed at different rates depending on the place of service. Make sure you understand the Medicare Physician Fee Schedule and how it applies to POS 49 services.
Medicaid Variations by State
Medicaid programs vary significantly by state. Some states have specific definitions for independent clinics and may require additional documentation when using POS 49. Always check your state’s Medicaid billing manual for guidance.
Private Insurance Considerations
Commercial insurance plans each have their own policies regarding POS 49. Some may:
- Require pre-authorization for certain services at independent clinics
- Have different copay structures for POS 49 versus POS 11
- Limit which types of services they’ll cover at independent clinics
Step-by-Step Guide to Billing with POS 49
Let’s walk through the proper process for using POS 49 in your medical billing workflow:
Step 1: Verify the Facility Type
Before you do anything else, confirm that the facility qualifies as an independent clinic. Check:
- Business structure and ownership
- Relationship to any hospital systems
- State licensing and registration documents
Step 2: Gather Complete Documentation
Collect all necessary information:
- Patient demographics and insurance details
- Complete service documentation from the provider
- Facility information including NPI and address
- Diagnosis codes that support medical necessity
Step 3: Select Appropriate CPT Codes
Match the services provided with the correct CPT (Current Procedural Terminology) codes. Remember, POS 49 is just the location—you still need accurate procedure codes.
Step 4: Enter POS 49 in Box 24B
On the CMS-1500 claim form, Box 24B is where you enter the place of service code. Enter “49” here for services provided at independent clinics.
Step 5: Review for Common Errors
Before submitting, double-check:
- Is POS 49 the correct code for this facility?
- Do all line items have consistent place of service codes?
- Does the documentation support the location stated?
- Are modifiers used correctly if applicable?
Step 6: Submit and Monitor
Submit the claim electronically when possible for faster processing. Track the claim status and be prepared to provide additional documentation if requested.
Best Practices for Accurate POS 49 Coding
Want to master POS 49 in medical billing? Follow these proven strategies:

Create a Facility Database
Maintain a reference list of all facilities where your organization provides or bills for services. Include:
- Facility name and address
- Correct POS code to use
- NPI number
- Any payer-specific requirements
Update this database regularly as facilities change ownership or structure.
Train Your Team Regularly
Medical billing rules evolve. Schedule quarterly training sessions that cover:
- Updates to POS code definitions
- Common coding errors and how to avoid them
- New payer policies affecting POS 49
- Real-world case studies
Implement Quality Checks
Build quality control into your billing process:
- Have a second set of eyes review claims before submission
- Run regular audits on POS code usage
- Track denial patterns related to place of service
- Create feedback loops so billers learn from mistakes
Stay Current with Industry Changes
Healthcare billing regulations change frequently. Keep yourself informed by:
- Subscribing to CMS updates and announcements
- Joining professional billing associations
- Attending webinars and conferences
- Reading industry publications regularly
Use Technology Wisely
Modern billing software can help prevent POS 49 mistakes:
- Set up validation rules that flag unusual POS combinations
- Create templates for common scenarios
- Use dropdown menus to reduce manual entry errors
- Generate reports that identify coding patterns
Troubleshooting POS 49 Claim Denials
Even with careful attention, you may encounter claim denials related to POS 49. Here’s how to handle them:
Common Denial Reasons
“Place of service inconsistent with procedure code”: Some procedures aren’t typically performed at independent clinics. Review the CPT code and POS 49 combination.
“Documentation does not support place of service”: The payer needs proof the service occurred at an independent clinic. Gather facility documentation.
“Provider not credentialed for this location”: The provider may need to be credentialed specifically for the independent clinic.
“Service not covered at this location”: The patient’s plan may not cover certain services when performed at POS 49 facilities.
Steps to Resolve Denials
- Review the denial reason code carefully: Understand exactly why the claim was rejected
- Gather supporting documentation: Collect everything that proves POS 49 was correct
- Check for coding errors: Sometimes the issue isn’t POS 49 itself but another code on the claim
- Contact the payer: If you believe the denial is incorrect, call for clarification
- Submit a corrected claim or appeal: Follow the payer’s process for resubmission
- Document the resolution: Keep records to prevent similar issues in the future
The Future of POS 49 and Medical Billing
Healthcare delivery continues to evolve, and so does medical billing. Here’s what might impact POS 49 in the coming years:
Expansion of Independent Clinics
The trend toward independent healthcare facilities shows no signs of slowing. As more clinics open outside traditional hospital systems, accurate use of POS 49 becomes increasingly important.
Value-Based Care Models
As healthcare shifts from fee-for-service to value-based care, place of service codes may play a different role in payment structures. Stay informed about how these changes affect your billing practices.
Technology Integration
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are being integrated into billing systems to catch coding errors before claims are submitted. These tools can help identify when POS 49 might be incorrect based on other claim data.
Regulatory Updates
CMS periodically reviews and updates place of service codes. While POS 49 has been stable, always watch for announcements about changes to definitions or usage guidelines.
Understood. Here is a short, impactful conclusion that quickly summarizes the main points and includes a professional closing, keeping the tone consistent with the rest of the guide:
Final Thoughts
The complexity of medical billing should never lead to claim denials, and mastering POS 49 in medical billing is critical to your revenue health. Remember the core concept: POS 49 applies exclusively to the Independent Clinic—separate from both a private office (POS 11) and a hospital.
Accuracy starts with verification, diligent documentation, and staying current with payer rules. By applying these strategies, you remove confusion, minimize costly errors, and ensure faster reimbursement for services delivered at independent facilities.
By applying diligent documentation and up-to-date strategies, you remove confusion and minimize costly errors.
If you’re looking to strengthen your POS 24 billing accuracy and maintain full compliance, RevenueES can help. Our experienced billing specialists ensure every outpatient surgery claim is properly coded, fully documented, and reimbursed at its true value. Connect with us today to enhance your billing performance and protect your revenue cycle.





